Power BI vs Amazon QuickSight (2025): Features, Pros & Cons
The business intelligence (BI) software market keeps expanding as companies move from static reporting to cloud-first, AI-assisted analytics. When teams shortlist platforms, Microsoft Power BI and Amazon QuickSight often lead the conversation. Both are modern and widely adopted, yet they differ in ecosystems, pricing models, and where they shine. This article clarifies what each tool is, how it works, when to choose it, and compares features, scalability, and cost patterns ' so you can pick the right fit in 2025.
What is Power BI?
Power BI is Microsoft’s flagship BI platform, tightly integrated with Excel, Microsoft 365, Azure, and now Microsoft Fabric capacities for enterprise scenarios. It’s popular across finance, retail, and healthcare, with strong self-service analytics and a large practitioner community.
In 2025, Microsoft is recognized as a Leader in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Analytics & BI for the 18th year in a row, underscoring its momentum in the category.
How does Power BI work?
Power BI connects to files (Excel/CSV), databases (SQL Server, Postgres), cloud sources (Azure, Salesforce, Google Analytics via connectors), and models data via Power Query and the DAX semantic layer.
Content is built in Desktop and shared via the Power BI Service. In 2025, licensing centers on Pro and Premium Per User (PPU), while capacity scenarios run on Microsoft Fabric.
Starting April 1, 2025, list prices are Pro $14/user/month and PPU $24/user/month (renewals align at the next term).
When to use Power BI
Choose Power BI when your organization is Microsoft-centric (Excel/M365/Azure), needs robust modeling (DAX), and benefits from rich visuals and governance in the same ecosystem.
Independent TEI research from Forrester cites a three-year ROI of ~366% tied to productivity and license consolidation—useful context for business cases.
What is Amazon QuickSight?
Amazon QuickSight is AWS’s cloud-native, fully managed BI service built to plug directly into Amazon Redshift, Athena, S3, RDS, and more. It emphasizes speed at scale, embedded analytics, and flexible pricing for large viewer populations. AWS states 100,000+ customers use QuickSight across industries.
How does Amazon QuickSight work?
QuickSight connects to AWS sources (and others), caches data via SPICE for fast performance, and serves dashboards to thousands of concurrent users. In 2025, Amazon Q in QuickSight brings generative capabilities (NLQ, summaries, scenario building) through Pro roles with an enablement fee of $250/account/month; Pro tiers are Author Pro $50/user/month and Reader Pro $20/user/month. Standard roles remain Author $24/user/month (or $18 on annual) and Reader $3/user/month, plus capacity (sessions) pricing starting at $250 for 500 sessions/month.
When to use Amazon QuickSight
Pick QuickSight if you run primarily on AWS, need to serve large numbers of readers, or plan embedded analytics in your apps.
The Reader and capacity options can be cost-efficient for wide distribution; Amazon Q accelerates insight generation for non-technical audiences and speeds authoring for analysts.
Power BI vs Amazon QuickSight: Feature Comparison Table
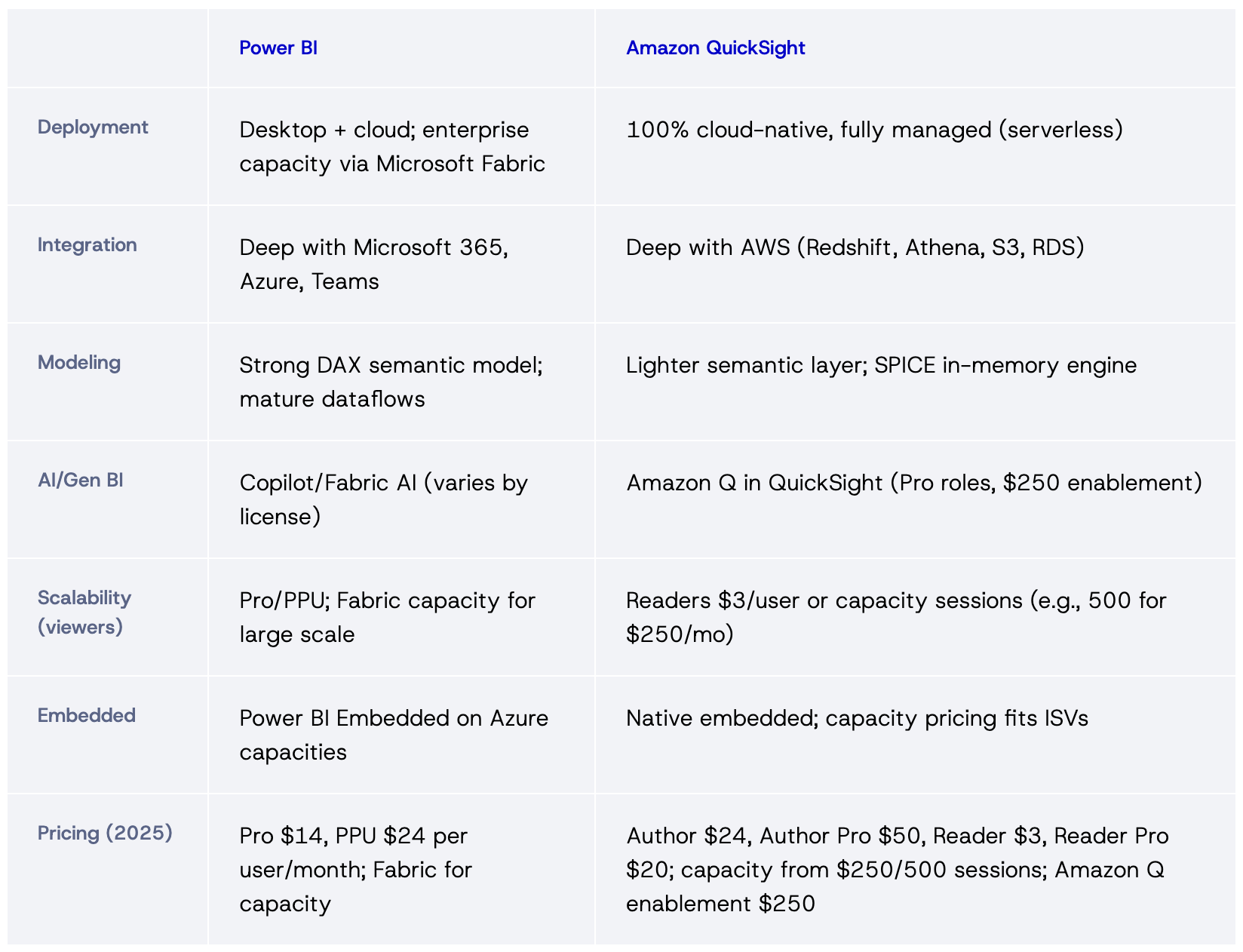
Power Bi and QS
If your company is built around Microsoft, Power BI is often the better fit. If you’re heavily invested in AWS or need cloud-native scalability and embedding, QuickSight is a natural choice.
Pros
Power BI
- Tight Microsoft ecosystem integration (Excel/M365/Azure) and broad community support.
- Mature modeling with DAX and powerful visual layer.
- Clear growth path from Pro/PPU to Fabric capacities when scaling.
- Independent study cites ~366% three-year ROI as a benchmark for business cases.
Cons
Power BI
- Enterprise-scale distribution often requires PPU or Fabric capacity planning.
- Advanced DAX/modeling has a learning curve; governance setup needs experience.
- Price adjustments effective April 1, 2025 impact budgets at renewal.
Pros and Cons of Amazon QuickSight
Pros
- Native AWS integration; fast path for Redshift/Athena/S3.
- Cost-flexible viewer options (Reader $3 or capacity sessions starting at $250/500 sessions).
- Amazon Q adds NLQ, summaries, and generative authoring for Pro roles.
Cons
- Less granular visual customization vs some competitors.
- Best experience inside AWS; outside ecosystems may need extra plumbing.
Amazon Q adds an enablement fee ($250/account/month) and Pro-tier costs for generative features.
Power BI or Amazon QuickSight: Which Should You Choose?
- Choose Power BI if you’re Microsoft-first, rely on Excel models, or need richer semantic modeling and visuals. The Pro → PPU → Fabric path covers most scales with consistent governance.
- Choose Amazon QuickSight if you’re AWS-first, need to reach many readers or embed analytics broadly, and want Amazon Q to speed insight generation and authoring. Capacity sessions help control viewer TCO.
Conclusion
Both tools are strong, but the right choice depends on your stack, audience size, and growth plan: Power BI for deep Microsoft alignment and modeling; QuickSight for AWS-native scale, embedding, and flexible viewer economics (with Amazon Q for generative workflows).
In 2025, align your BI platform with your broader IT strategy and distribution needs - there’s no universal winner.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: What is Power BI used for? Power BI is used to build interactive dashboards and reports, especially in Microsoft-centric environments (Excel/M365/Azure), with strong modeling via DAX.
Q2: Is Power BI free? Power BI Desktop is free for authoring; collaboration and sharing require Pro or PPU, with new list prices $14 and $24 per user/month from April 1, 2025.
Q3: What is Amazon QuickSight used for? QuickSight serves cloud-native analytics on AWS, connecting to Redshift/Athena/S3, scaling to large audiences, and supporting embedded use cases; Amazon Q adds generative features.
Q4: How does Amazon QuickSight pricing work? Per-user (Author $24, Reader $3) or capacity sessions (e.g., $250 for 500 sessions/month). Generative features via Author/Reader Pro and Amazon Q enablement fee $250/account/month.
Q5: Power BI vs Amazon QuickSight – which is better? It depends on your environment: Power BI for Microsoft-aligned orgs and heavier modeling; QuickSight for AWS-centric teams and wide distribution/embedding.
Q6: Can Power BI connect to AWS data sources? Yes—Power BI can connect to Redshift/S3 and others via connectors, though QuickSight is more seamless for AWS-native stacks.
Q7: Does Amazon QuickSight support Excel? Yes—QuickSight can import Excel/CSV; Power BI has the edge for native Excel workflows due to Microsoft 365 integration.
Interesting For You

How to Get the Most Out of Amazon Redshift: A Practical Guide for Analytics Teams
Why tuning your Redshift setup pays off more than you think Redshift Is Powerful — But Only If You Know How to Use It Amazon Redshift is one of the most widely adopted data warehouses for a reason. It’s scalable, relatively affordable, and tightly integrated with the AWS ecosystem. But too often, analytics teams treat it as a black box — dumping data in and hoping it performs well. In reality, Redshift gives you a lot of control over how your data is stored, distributed, and queried. And if you don’t take advantage of those features, performance issues can creep in fast — especially as your data grows. This article breaks down the most common issues BI teams face with Redshift and shows how to optimize your setup for real-world analytics — without throwing more hardware (or budget) at the problem.
Read article

Designing BI for Speed: Modeling Patterns that Cut Query Time by 30–60%
Slow dashboards aren’t inevitable. Most delays come from a handful of fixable choices in modeling and SQL. This article outlines a practical approach for mid-market teams in e-commerce, retail, and manufacturing: shape the data for analysis, pre-compute what’s heavy, and keep queries friendly to the engine. You’ll find concrete patterns, a 30-day plan, and simple signals to track whether performance is actually improving.
Read article

Unlocking the Power of Data: ETL and Real-Time Architectures
Turning raw data into actionable insights is a cornerstone of modern business strategy. But achieving this requires more than one-size-fits-all solutions. ETL pipelines remain indispensable for historical data processing and analytics. However, when low-latency decisions and real-time responsiveness are critical, event-driven architectures and streaming data approaches take center stage.
Read article